Plugin for Nexus¶
Installing the plugin¶
The CodeScoring.OSA plugin comes as a JAR file and supports the following Sonatype Nexus Repository versions:
nexus-codescoring-plugin-{release}.jar- for Nexus Repository Community Edition versions from 3.71 to 3.77 and Nexus Repository Pro versions from 3.33.1-01 to 3.77 (supports H2 and PostgreSQL);nexus-codescoring-plugin-legacy-{release}.jar- for Nexus Repository OSS versions from 3.33.1-01 to 3.70.Х (supports OrientDB).
To add a plugin to NXRM you must:
- Copy the
nexus-codescoring-plugin.jarfile received from the vendor to the/opt/sonatype/nexus/deploydirectory: If NXRM is running in a Docker container: - Grant rights for the user and group
nexus: If NXRM is running in a Docker container: - Check that the user has a minimum set of privileges to work correctly with the plugin:
After the completed operations, you need to restart NXRM.
Plugin setup¶
To use the CodeScoring.OSA plugin in further work, you must use the Capability mechanism provided by NXRM. Capability is a set of APIs and UI components for embedding into NXRM, allowing you to expand its functionality.
The CodeScoring.OSA plugin provides four new Capabilities:
- CodeScoring Configuration — setting up interaction with the on-premise platform of CodeScoring;
- CodeScoring Scan — setting up scanning for a separately selected proxy repository;
- CodeScoring Docker Repository Scan – setting up scanning for a separately selected hosted or proxy docker repository;
- CodeScoring All Repositories Scan – scan settings for all repositories.
After installing the CodeScoring.OSA plugin in the System -> Capabilities section, it will be possible to create Capability through the (+ Create capability) interface element.
CodeScoring Configuration¶
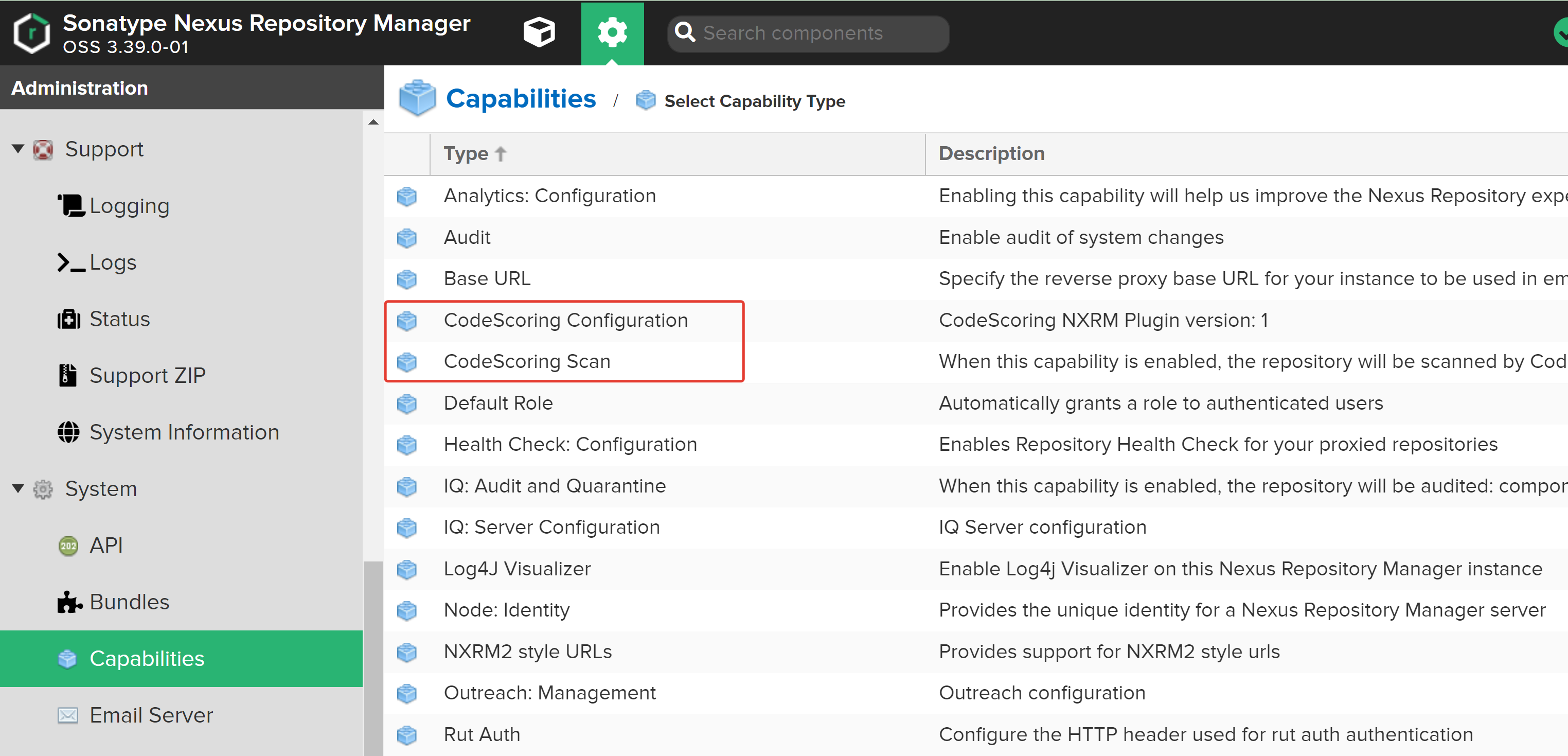
This extension allows you to set general plugin settings for working with the CodeScoring platform:
- CodeScoring URL – address of the on-premise platform of CodeScoring;
- CodeScoring Token – key for authorizing API calls (Created from CodeScoring section
Profile -> Home); - HttpClient Connection Pool Size – number of available connections. This parameter allows you to control the number of parallel requests to speed up scanning;
- Timeout for CodeScoring requests in seconds – time to wait for a response from the platform (in seconds, default value is 1800);
- HTTP Proxy Host – proxy server address. Used if it is not possible to establish a direct connection between NXRM and CodeScoring;
- HTTP Proxy Port – proxy server port;
- Block downloads in case of plugin or CodeScoring errors – blocking the download of a component if there are errors from the plugin or CodeScoring API.
- Custom message for blocked packages – message for the user when components are blocked;
- Nexus URL for identification in CodeScoring – address of the Nexus Repository Manager with the protocol for displaying the results on the platform.
Required fields
The CodeScoring URL, CodeScoring Token, HttpClient Connection Pool Size, Timeout for CodeScoring requests in seconds, and Nexus URL for identification in CodeScoring fields are required.
Attention: the specified settings will be used by all instances that check proxy repositories.
CodeScoring Proxy Repository Scan¶
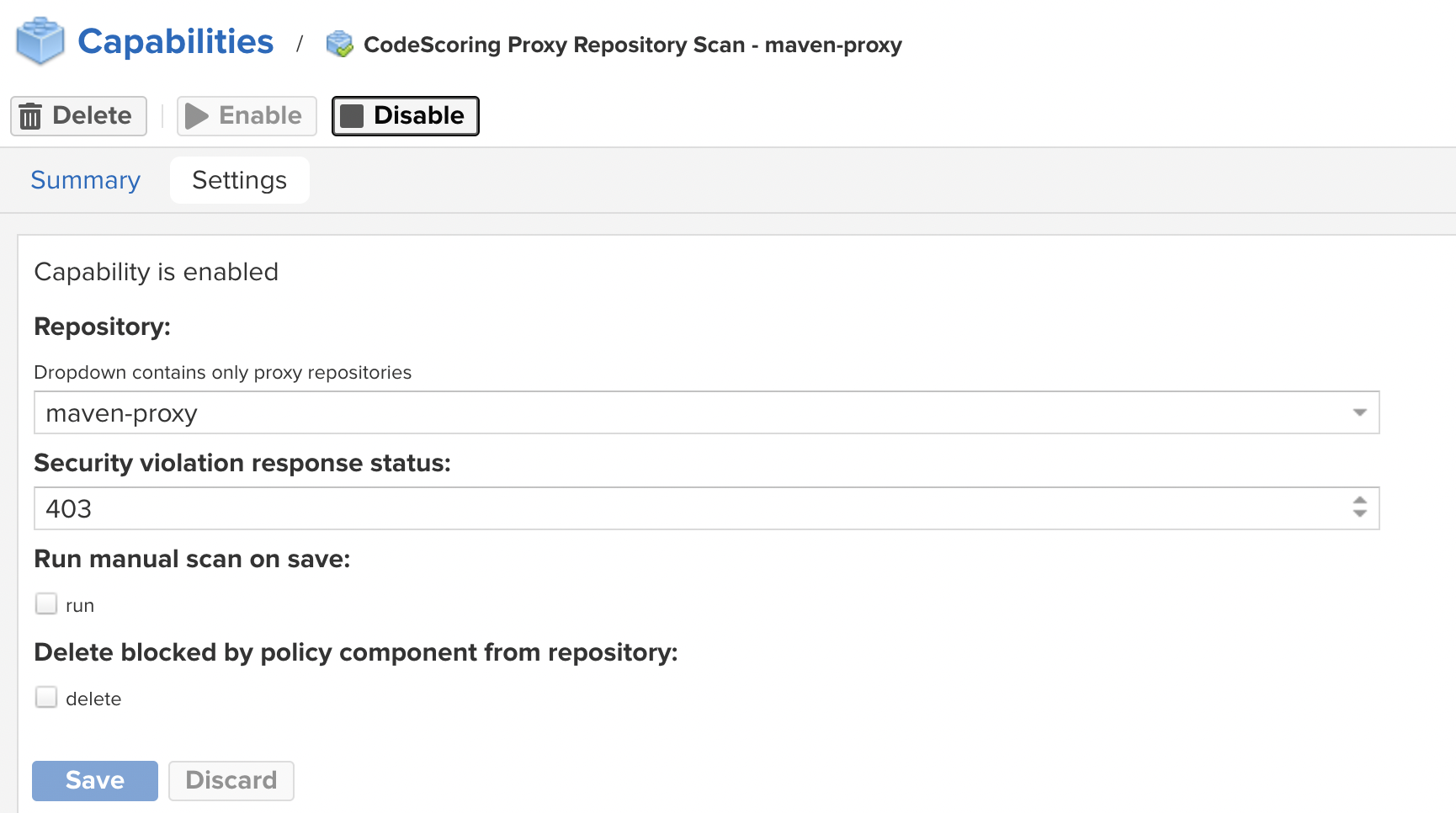
This extension allows you to enable component checking for the selected proxy repository with the following parameters:
- Repository – select the repository for which the escaping function will be applied;
- Security violation response status – error code returned when security policies are triggered;
- Delete blocked by policy component from repository – forced removal of blocked components from the repository (creating a “sterile” repository);
- Select capability work mode – plugin operating mode.
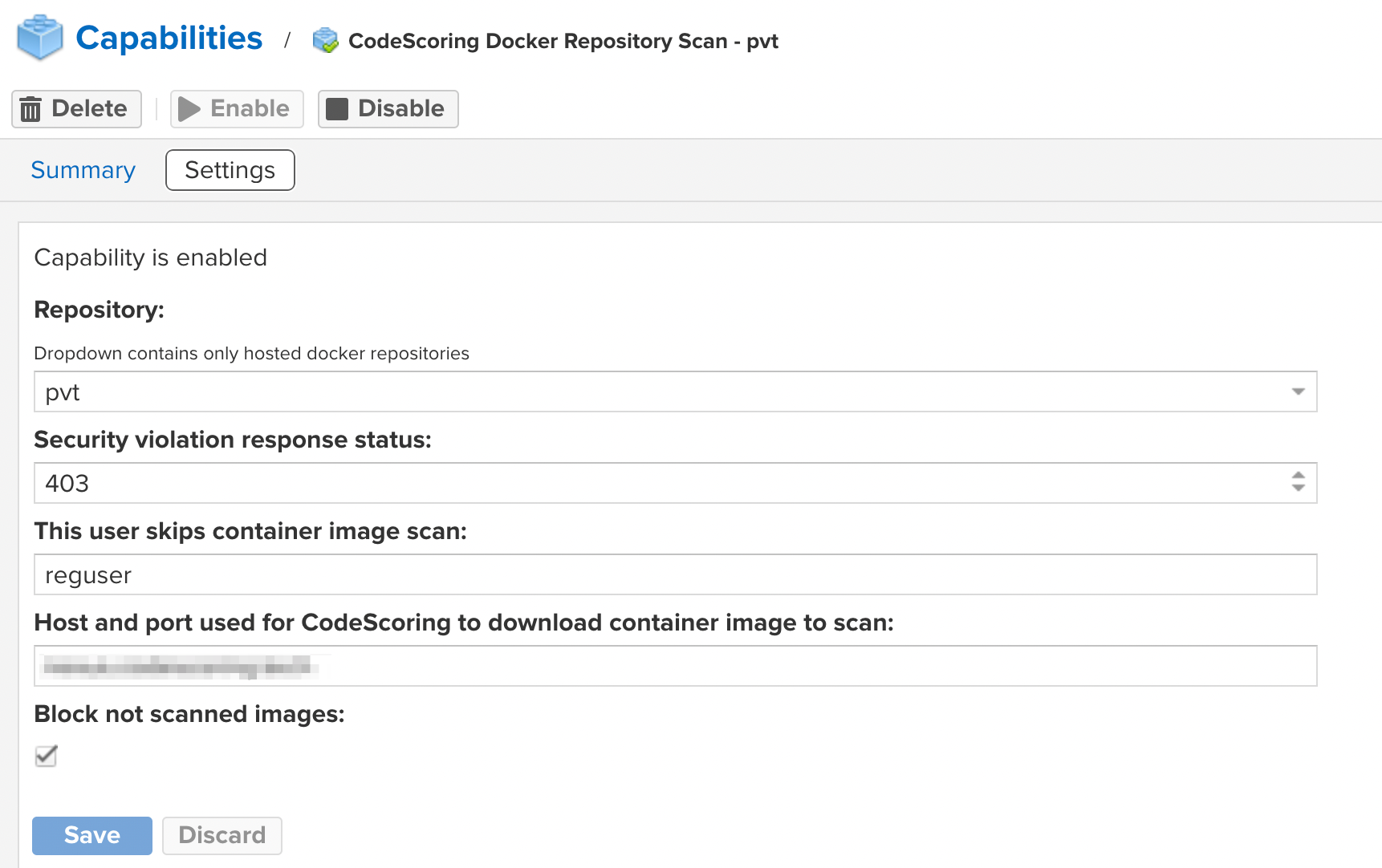
CodeScoring Docker Repository Scan¶
This extension allows you to enable component check for the selected hosted or proxy docker repository with the following parameters:
- Repository – select the repository for which the escaping function will be applied;
- Security violation response status – error code returned when security policies are triggered;
- This user skips container image scan – user for which image scanning is not applied. Used when loading and checking components by the console agent;
- Container registry host as used in the
docker pull host/image_namecommand – address (without specifying the protocol) and port through which images for scanning will be downloaded. Used to communicate between Nexus and repository via Docker; - Select capability work mode – plugin operating mode. The operating modes are described in the section below;
- Append repository name to image name for Docker repositories – adding the repository name to PURL for correct operation in RepoPath mode (in case of accessing the component via the
docker pull registry/repository/image_namecommand).
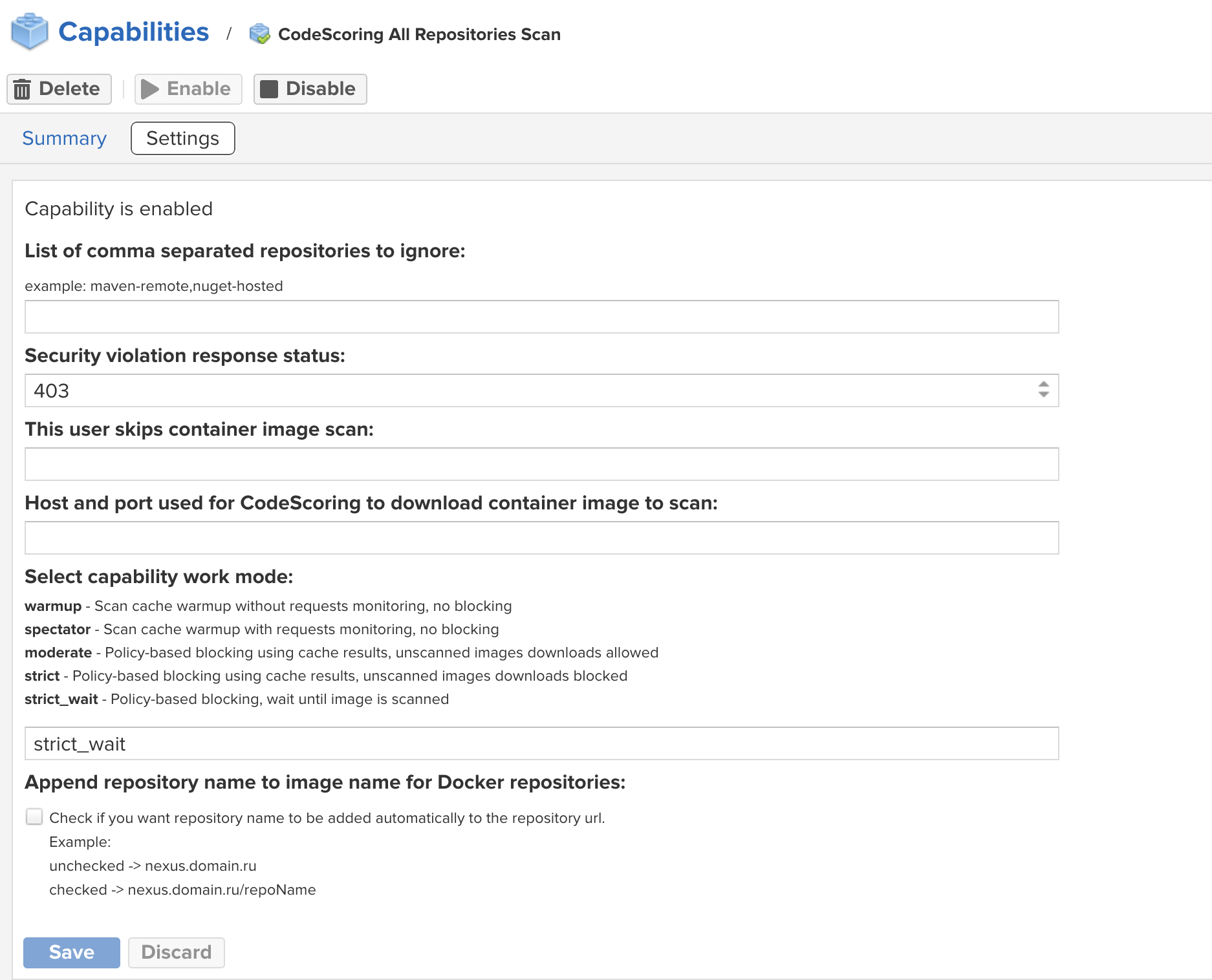
CodeScoring All Repositories Scan¶
The extension allows you to enable component checking for all repositories within the Sonatype Nexus Repository Manager with the following parameters:
- List of comma separated repositories to ignore – list of repositories that will not be scanned;
- List of comma separated repository formats to scan – list of repository formats to scan. Available formats:
maven2,npm,pypi,nuget,cocoapods,go,rubygems,conan,apt,yum,apk,docker; - Security violation response status – error code returned when security policies are triggered;
- This user skips container image scan – user for which image scanning is not applied. Used when downloading and checking components by the console agent;
- Container registry host as used in the
docker pull host/image_namecommand – address (without specifying the protocol) and port through which images for scanning will be downloaded. Used to communicate between Nexus and repository via Docker; - Select capability work mode – plugin operating mode. The operating modes are described in the section below;
- Append repository name to image name for Docker repositories – adding the repository name to PURL for correct operation in RepoPath mode (in case of accessing the component via the
docker pull registry/repository/image_namecommand).
Setting the plugin operating mode¶
The operating mode of the plugin must be defined as a text string in the corresponding field of the Capability CodeScoring Proxy Repository Scan and Capability CodeScoring Docker Repository Scan settings.
The plugin has 5 operating modes that determine the severity of component checking before loading.
- warmup – loading data into the CodeScoring cache without blocking components;
- spectator – loading data into the CodeScoring cache without blocking components, saving the results of component queries to the platform;
- moderate – blocking components that have not passed the policy check. Loading of unscanned components is allowed;
- strict – blocking components that do not pass the policy check. Loading of unscanned components is prohibited;
- strict_wait – blocking components that have not passed the policy check. Pending verification for unscanned components.
Setting up logging¶
To configure logging of plugin events, you need to go to the Support -> Logging section and add a logger with the name ru.codescoring and logging level DEBUG.
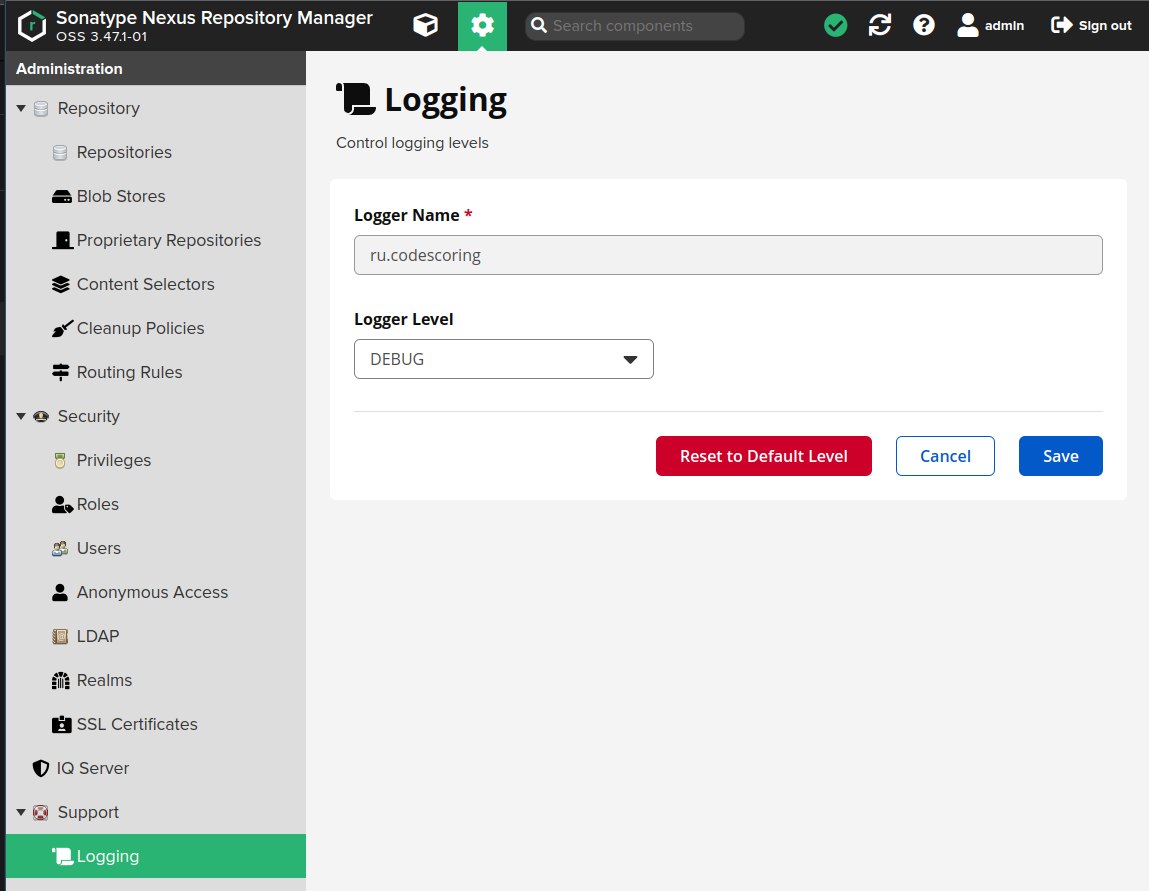
Event logging results are available in the Support -> Logs section.
Blocking components¶
When a component is blocked from downloading, the user console displays one of the following reasons for blocking:
- "The download has been blocked in accordance with the policies configured in CodeScoring" – blocking of the component according to the policies configured on the platform;
- "The component has not yet been scanned by CodeScoring, it is scheduled to be scanned shortly. The download is blocked according to the plugin settings" – blocking an unscanned component and then starting scanning. Used in
strictmode; - "The download has been blocked due to the failure of the scan of the component in CodeScoring" – the component could not be scanned;
- "The download has been blocked due to the wrong mode of the plugin" – incorrect [plugin operating mode] is used(#_3);
- "The download has been blocked due to the timeout of the scan of the component in CodeScoring" – the timeout for scanning the component has expired. Used in
strict_waitmode; - "The download has been blocked, because registry is not configured in CodeScoring" – there is no corresponding Registry in the platform.
The response also contains a link to the component page in CodeScoring with information about triggered security policies and found vulnerabilities:
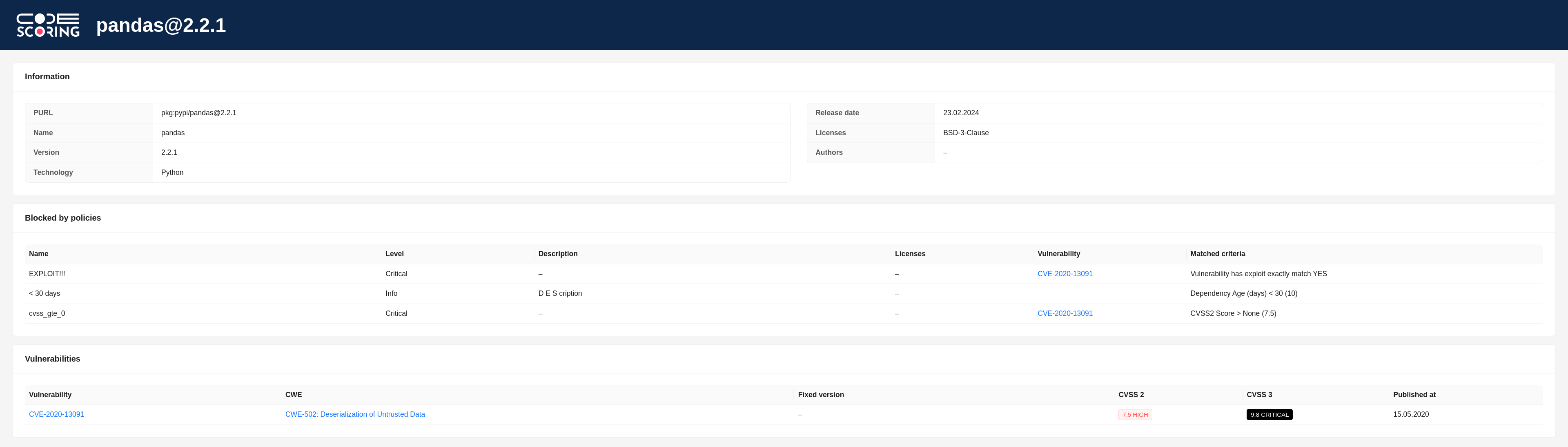
Setting up an SSL connection¶
To set up an SSL connection between the plugin and the platform, you need to import certificates into the Java Truststore.
Finding the location of your Java platform¶
To import certificates into the Java Truststore, you first need to locate your Java installation. This can be done in one of the following ways:
-
Using the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable: -
Using the
javacommand with the-XshowSettings:propertiesparameter: -
Using the
readlinkcommand with the path tojava:
The following steps assume that the $JAVA_HOME variable is set.
Downloading the certificate¶
You can download the certificate with the following command:
openssl s_client -connect <codescoring.domain.ru>:443 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 > codescoring_ca.pem
Make sure you replace <codescoring.domain.ru> with the corresponding address of your platform.
Importing a certificate¶
Once the certificate has been downloaded, it can be imported into the Java Truststore using the following command:
keytool -import -alias <mycert> -keystore $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts -file <codescoring_ca.pem>
Notes:
- Replace
<mycert>with a unique name for your certificate. - Replace
<codescoring_ca.pem>with the actual name of your certificate file. - You may be asked to enter a password for the Truststore. The default password is
changeit.
Verifying the import¶
To verify that the certificate was successfully imported, use the keytool command to list the certificates in the Truststore:
Note:
- You can use the
grepcommand to filter the results by your certificate alias:
Working with system packages¶
Setting up repositories¶
For plugin to work correctly with system packages of some ecosystems, additional actions must be taken.
For the plugin to work correctly, you must specify the codename of the distribution from the remote repository, for example "bullseye" for Debian. This name is used in PURL (Package URL) to improve the accuracy of package analysis.
The codename should be in lowercase and without extra symbols.
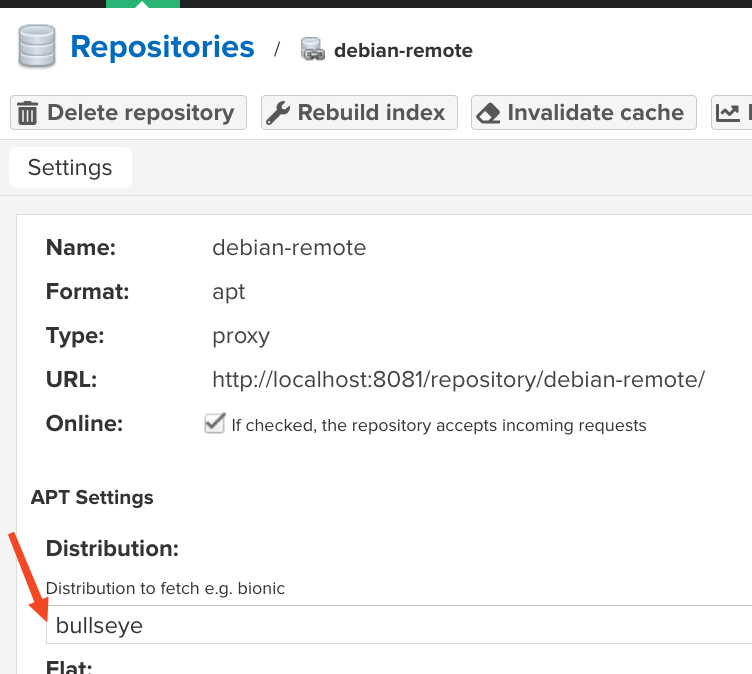
List of supported Debian distributions:
- Debian 2.0 – hamm
- Debian 2.1 – slink
- Debian 2.2 – potato
- Debian 3.0 – woody
- Debian 3.1 – sarge
- Debian 4 – etch
- Debian 5 – lenny
- Debian 6 – squeeze
- Debian 7 – wheezy
- Debian 8 – jessie
- Debian 9 – stretch
- Debian 10 – buster
- Debian 11 – bullseye
- Debian 12 – bookworm
- Debian 13 – trixie
- Debian 14 – forky
List of supported Ubuntu distributions:
- Ubuntu 4.10 – warty
- Ubuntu 5.04 – hoary
- Ubuntu 5.10 – breezy
- Ubuntu 6.06 – dapper
- Ubuntu 6.10 – edgy
- Ubuntu 7.04 – feisty
- Ubuntu 7.10 – gutsy
- Ubuntu 8.04 – hardy
- Ubuntu 8.10 – intrepid
- Ubuntu 9.04 – jaunty
- Ubuntu 9.10 – karmic
- Ubuntu 10.04 – lucid
- Ubuntu 10.10 – maverick
- Ubuntu 11.04 – natty
- Ubuntu 11.10 – oneiric
- Ubuntu 12.04 – precise
- Ubuntu 12.10 – quantal
- Ubuntu 13.04 – raring
- Ubuntu 13.10 – saucy
- Ubuntu 14.04 – trusty
- Ubuntu 14.10 – utopic
- Ubuntu 15.04 – vivid
- Ubuntu 15.10 – wily
- Ubuntu 16.04 – xenial
- Ubuntu 16.10 – yakkety
- Ubuntu 17.04 – zesty
- Ubuntu 17.10 – artful
- Ubuntu 18.04 – bionic
- Ubuntu 18.10 – cosmic
- Ubuntu 19.04 – disco
- Ubuntu 19.10 – eoan
- Ubuntu 20.04 – focal
- Ubuntu 20.10 – groovy
- Ubuntu 21.04 – hirsute
- Ubuntu 21.10 – impish
- Ubuntu 22.04 – jammy
- Ubuntu 22.10 – kinetic
- Ubuntu 23.04 – lunar
- Ubuntu 23.10 – mantic
- Ubuntu 24.04 – noble
- Ubuntu 24.10 – oracular
- Ubuntu 25.04 – plucky
Browsing Debian package information¶
Plugin extracts package information from various sources. Specifically, it gets the package name, version, and architecture from the asset's Summary field. If the Summary is missing, the data for the PURL is parsed from the Path.
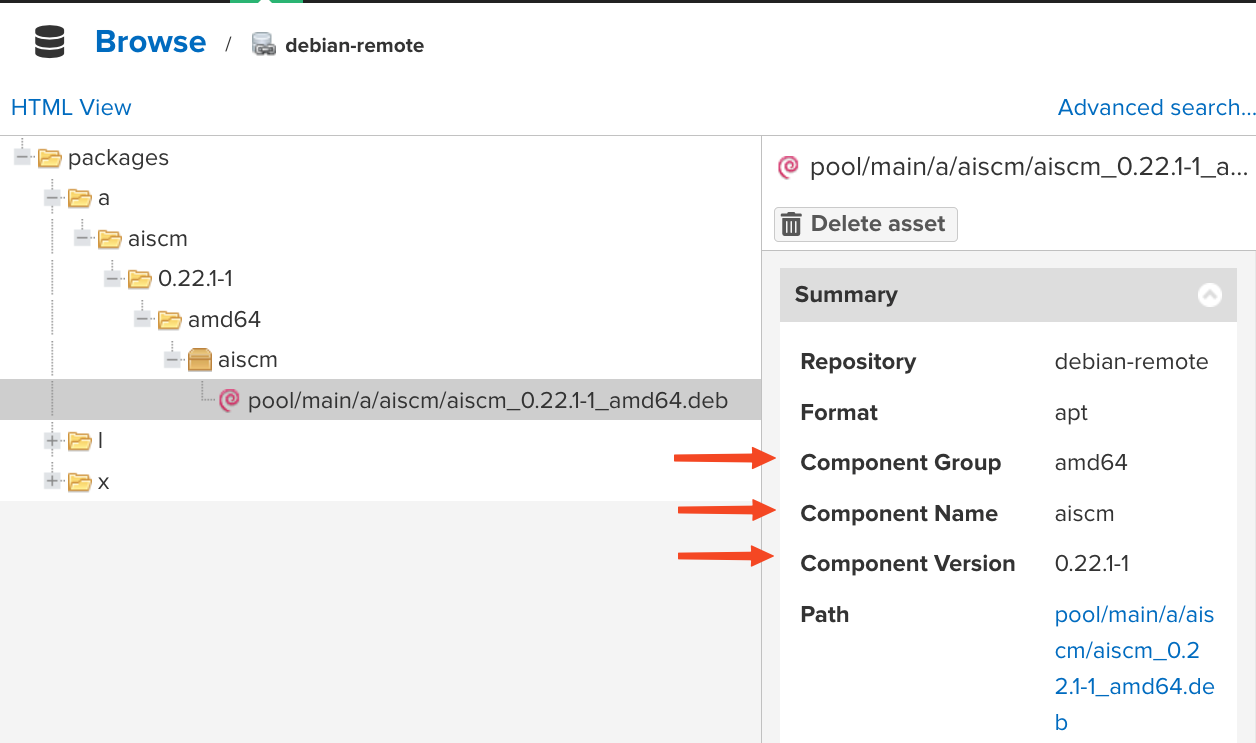
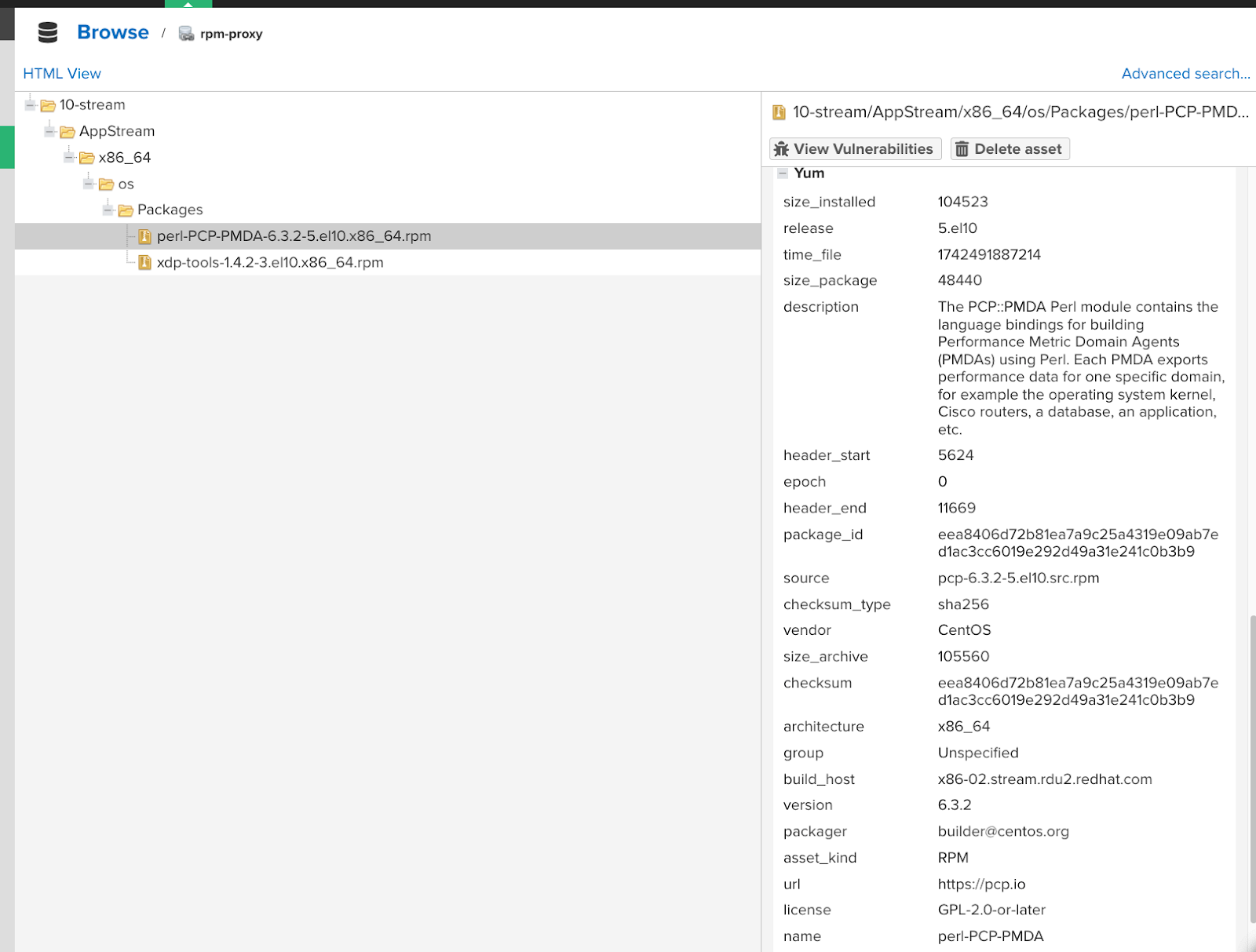
Browsing RPM package information¶
For RPM packages, plugin extracts data from the asset's attributes. This includes the package name, version, and architecture.