Overviewing dependencies¶
Viewing dependencies list¶¶
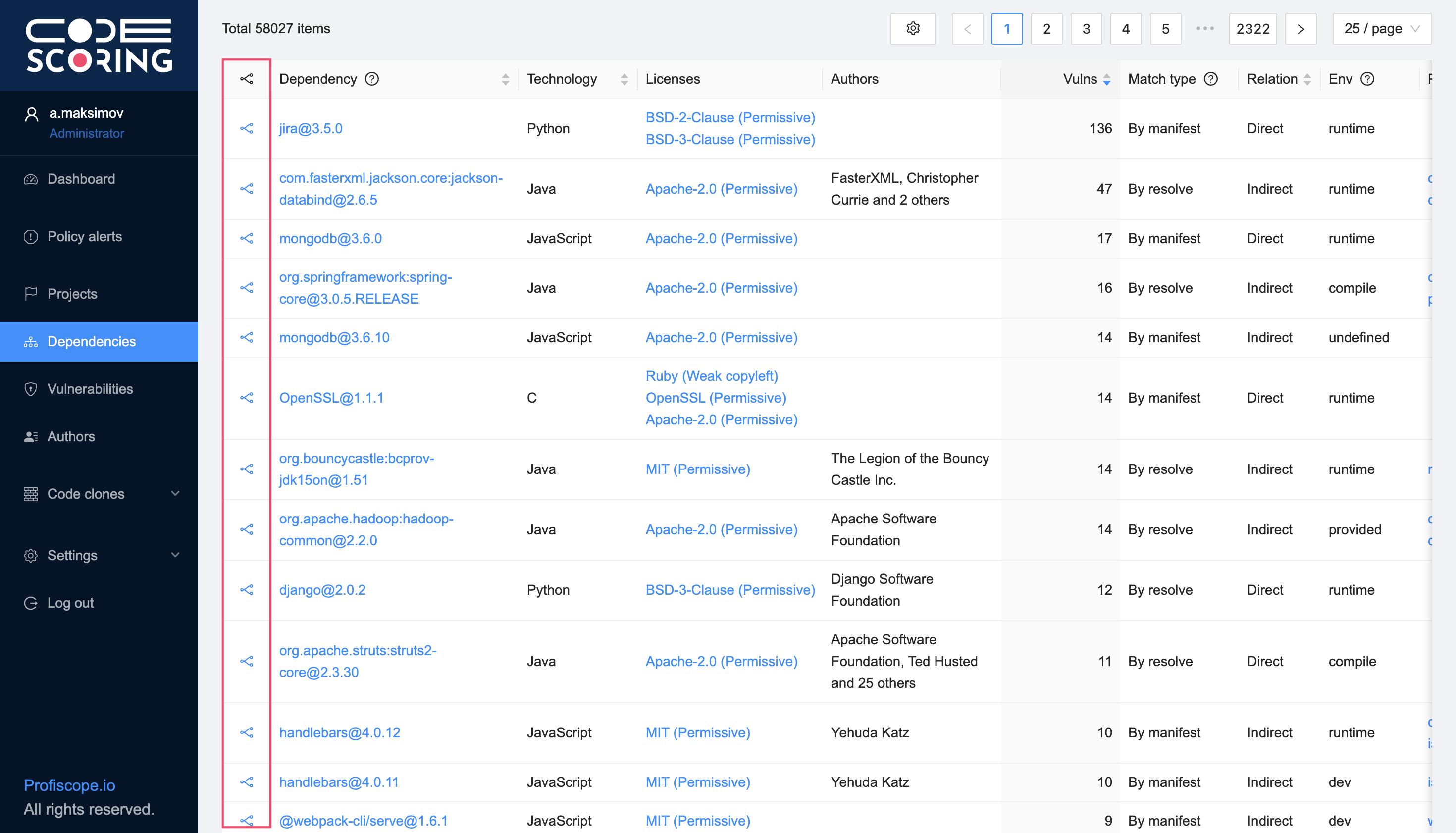
The list of scanned open source dependencies can be viewed in the SCA -> Dependencies subsection. The table in this section contains all dependencies that were checked during the operation of the SCA module, with the following information:
- Dependency – dependency name (with a link to its individual page);
- Technology – technology (programming language or build tool);
- Licenses – license ID from the package index;
- Authors – developer of the component the package index;
- Vulnerabilities – number of vulnerabilities found in the dependency;
- Found – dependency definition type: by resolve, by manifest or by content (when the component code is included in the project code base);
- Relationship – dependency type (direct or transitive);
- Environment – development environment;
- Parent Dependencies – related upstream dependencies;
- Project – project that uses the dependency;
- Maximum fix version - the version of the dependency to which an update should be performed in order to fix the vulnerabilities currently detected by the SCA module, while only dependencies with the specified fixed version are taken into account;
- Release date - the date and time of the dependency release.
The dependency table can be filtered by project, department, project category, project groups, technology, license, license category, as found, relationship, environment, release time period.
Clicking on the dependency name takes you to its individual page, where information about its use in projects and found vulnerabilities is displayed.
Working with dependency graph¶
Open source dependencies of software projects represent a graph – a structure in which individual components are depicted as nodes, and the connections between them as edges.
You can see the visualization of the dependency graph in the Dependencies section or on the project page by clicking on the corresponding icon in the list of dependencies.
On the page with interactive visualization, components are displayed according to their nesting level - from the root dependency to the deepest level of transitive dependencies. Hovering the cursor over an object reveals more detailed information about the component, such as version, environment, technology and number of vulnerabilities.
The visualization is interactive and scalable. By selecting a component, you can trace its path into the project. Components with identified vulnerabilities are highlighted.
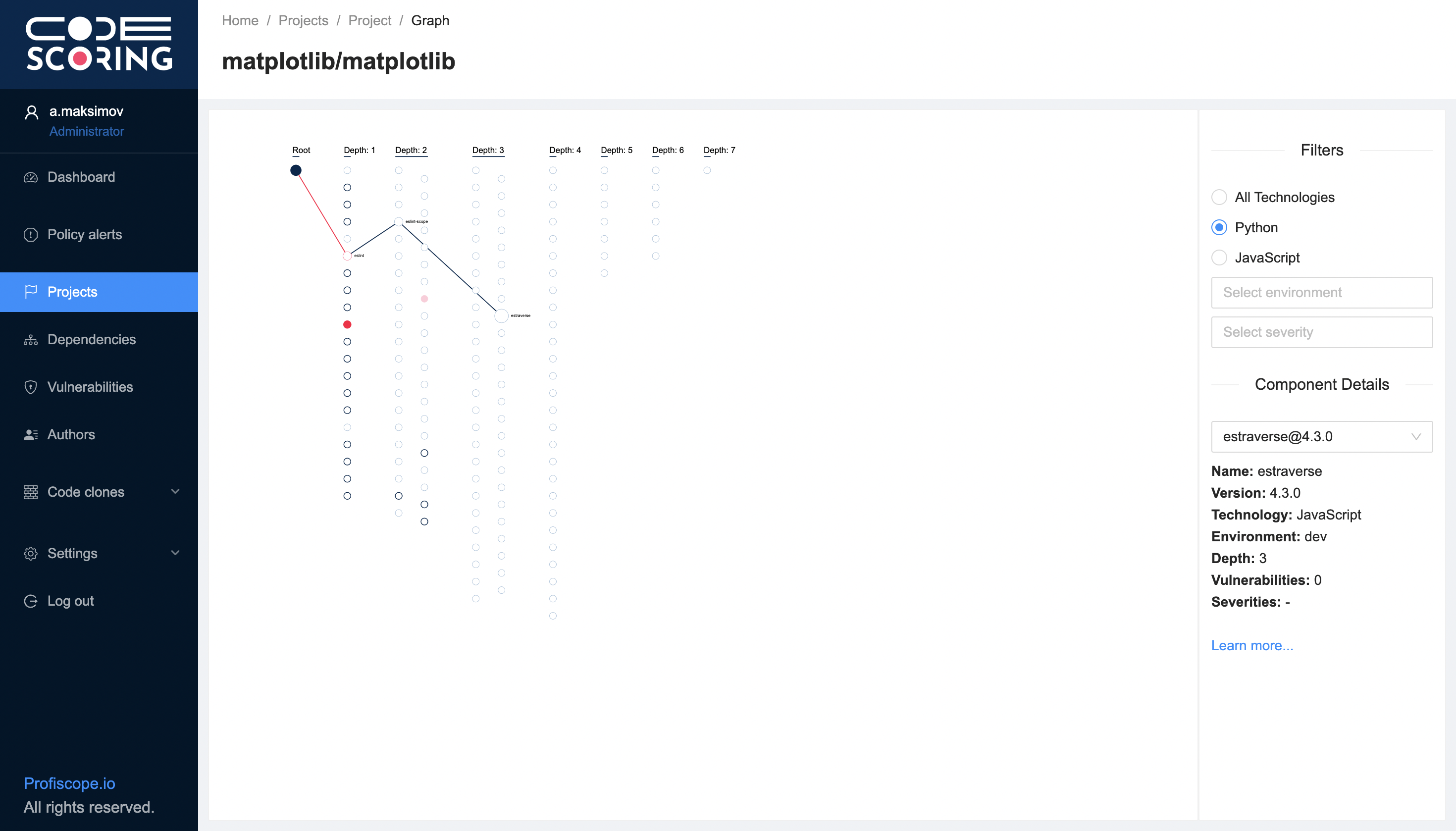
Components on the graph can be filtered according to the following parameters:
- technology;
- development environment;
- severity of vulnerability.